In this article, we explain different types of cracks in concrete, principal causes of cracks and remedies measures. Difference between structural cracks and non-structural cracks and so more.
Table of Contents
Cracks in Concrete:
Cracks appear in the structural member when the reaction force exceeds its capacity. These reactions force are caused by external loads like Dead Load, Live Load, Wind Load, Seismic Load, Foundation Settlement and internal forces such as thermal movements, moisture changes, chemical action etc.
Cracks can be divided into two main groups.
- Non-structural cracks
- Structural cracks
| Structural cracks | Non-structural cracks |
|---|---|
| Structural cracks are mainly due to defective design, defective construction, and due to excessive load on a building. | Non-structural cracks are mainly produced due to the internal reaction force of structural members. |
| Structural cracks are hazardous for the safety of construction. | Non-structural cracks are not hazardous to the safety of construction. |
| Ex. Cracks in RCC column or in a RCC beam. | Ex. Vertical cracks appear in Compound wall due to temperature changes. |
Cracks can be classified as follows on the basis of durability and width of serviceability:
- Thin – narrower than 1 mm.
- Medium – 1mm to 2 mm wide
- Wide – Cracks larger than 2 mm
- Cracks has straight, toothed, stepped, map pattern or random.
- Cracks are vertical, horizontal or diagonal.
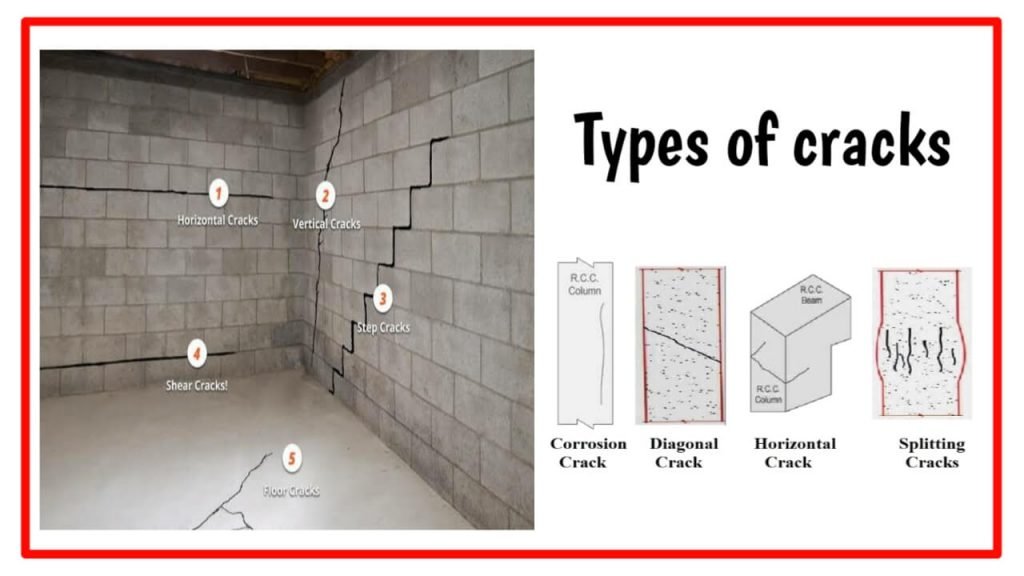
The internal reaction force in the structural members are compressive, tensile or shear type. Masonry, concrete or mortar are Strong in compression But weak in tension or shear.
This causes cracks in the structural member due to tension or shear.
Do You Know: Arrangement of Transverse Reinforcement in Column
Principles Causes of Cracks and Remedial Measures:
The main causes of cracks in houses are as follows:
- Moisture movement.
- Thermal movement
- Elastic deformation
- Creep
- Chemical reaction
- Foundation movement and settlement of soil
- Vegetation
1. Moisture movement:
Most building materials such as concrete, bricks, mortar, stones, wood, etc. expand and shrink as moisture enters. This movement is reversible.
When the cement based product dries, the absorbed water is first removed, thus reducing the size and shrinking of concrete. This type of contraction is variable. But as capillary water is removed from such a cement product, the size decreases and shrinkage occurs which is irreversible.
All porous materials expand when exposed to water and shrink as water is removed. But, irreversible compression occurs only once in the product, during construction.
The initial shrinkage in cement concrete or mortar depends on the following factors.
Also Read: What is Urban Heat Island Effect
Cement ratio:
The higher the cement content in the mix, the higher the shrinkage. On the other hand, the shrinkage decreases as the size of the aggregate increases in the mix.
Water content:
As the amount of water in the concrete increases, the shrinkage increases.
Aggregate:
If the maximum possible size of aggregate and good grading is used in concrete, the water requirement decreases for the required workability. Due to that the porosity of the concrete decreases and the shrinkage decreases.
Use of Accelerator:
Calcium chloride used as a accelerator in concrete. If the level of calcium chloride increases from 0.5 to 2.0%, the Shrinkage increases by 50%.
Curing:
Drying shrinkage is reduced if the concrete is cured properly for 7 to 10 days. Steam curing reduces shrinkage.
Also Read: Slate is a Natural Sustainable Building Material
Excessive fine aggregates:
Using excessive fine aggregates such as silt, clay, dust, etc. increases the specific surface area of the aggregate so that water requirement increases and Shrinkage increases.
The proportion of fine aggregate (silt, clay, dust) in the aggregate should not exceed 3%.
Humidity:
The relative humidity is high in coastal areas causing reduce shrinkage.
Temperature:
As the temperature of fresh concrete increases, the water requirement increases and shrinkage of concrete increases.
What is a Shrinkage cracks in concrete?
Tensile stress produces in a concrete due to contraction of concrete, bricks, or mortar.
If this tensile stress is greater than material strength, causing cracks in a material. Such cracks is known as a shrinkage cracks.
Remedies to prevent shrinkage cracks in building:
- The masonry should be plastered after curing for a sufficient time.
- if mortar is plastered with Cement:lime:sand (1: 1: 6, 1: 1: 9) which is reduces the shrinkage cracks in concrete.
Do You Know: What is Monolithic Construction Technology
2. Thermal Variations:
It is a well-known law of science that each material expands and shrinks as the temperature decreases or increases.
ut, if there is a barrier to this expansion or contraction therefore internal stress arises in the material and causes cracks in concrete due to tension or shear.
The daily temperature change in India is 5° C to 20° C and the annual temperature change is 0° C to 25° C.
The temperature coefficient of the thermal expansion of brick masonry is 50% higher than the horizontal direction in the upward direction, as there is no impediment to expansion in the upward direction.
Expansion in the upward direction is reversible while expansion in the horizontal direction is not reversible.
The following examples are needed to prevent cracks in concrete caused by temperature changes:
- The top slab in a load-bearing structure undergoes expansion due to sun heat and shrinkage due to reduced radiation heat. So that horizontal cracks fall in the horizontal walls.
- A protective cover or insulating cover should be made over the slab to prevent these cracks in concrete.
- The roof slabs, beams, columns move together in the fame structure. So that the diagonal cracks occur in walls that are parallel to the direction of movement. And the horizontal cracks occur in walls that are perpendicular to the direction of movement.
- Due to expansion in the compound wall, the coping of the stone rises in the middle and the horizontal cracks appear. To prevent these cracks, expansion joints should be placed at some distance in the wall.
- When two or more residential houses of more than 20 m length are constructed in a row, expansion joints should be placed between the two blocks for temperature expansion.
Also Read: Precast Concrete Vs Site cast Concrete
3. Elastic deformation:
Elastic deformation occur when building elements like slabs, beams, columns which are made of masonry, concrete, steel etc. are stressed. And elastic deformation causes cracks in concrete.
When the load on the walls is not evenly distributed, different stresses are produced in different parts and cracks appear.
When the span of a beam or slab is long and the load at the end is low, deflection causes cracks in the support walls.
Cracks occur when there is a big difference in the elastic properties of two materials and when two such materials are used side by side in construction.
4. Creep:
A constant load coming on building materials such as concrete, brick masonry, wood, etc., causes elastic deformation and long-term slow deformation in a building. This long-term slow deformation is called creep.
Creep depend on the amount of water and cement in the concrete, water-cement ratio, temperature, humidity, age of the concrete, etc.
If there is weak mortar used in brick masonry. Creep occurs more.
Creep causes deformation in building. Due to that cracks occur in the concrete.
The following measures should be taken to prevent cracks in concrete from creep, elastic deformation and shrinkage:
- Use of low shrinkage and low slump concrete.
- Construct building with proper quality control.
- Masonry should not be done before removing centering on beams or slabs. Masonry should be done 2 weeks after removal of centering.
- When RCC and masonry are to be plastered together, RCC and masonry should be allowed to dry for one month.
- The centering of the cantilever slab or beam should be removed as late as possible and the load on it should be given as late as possible.
- Everything should be completed before starting masonry in the fame structure.
- A horizontal movement joint should be provided at the top of the wall and at the bottom of the beam.
- An upward camber should be provided to reduce deflection in the beam or slab.
- Horizontal steel rods should be placed in high partition walls.
- Doors should be placed in the middle part (not at the corners) of the walls as far as possible
Also Read: What is Slurry Wall Construction
5. Chemical Reaction:
The main chemical processes are as follows:
- Sulfate attack
- Corrosion of Reinforcement
- Alkali Aggregate reaction.
Measures to prevent the effects of the chemical reaction:
- For concrete used in foundation, if the soil has a sulfate content of more than 0.2% or water sulfate content exceeds 300 rpm, high density concrete or sulfate resisting cement should be used.
- Bricks used in superstructures should not have more than 3% soluble salts per annum.
- Expansion joints should be placed in compound wall or parapet wall.
- Gypsum plaster should not be used.
6. Foundation movement and settlement of soil:
When the bearing capacity of soil is varying for different parts of building or soil bearing capacity is less than the load coming from the foundation. At that situation settlement of soil occurs due to excessive load. It is causes cracks in a building and sometimes it is also responsible for the failure of the foundation.
In such a situation, the design of the structure should be done keeping in view the engineering principles and good practice.
7. Vegetation:
Development of vegetation such as crops, plants, small trees, roots of trees, etc. below the foundation, near the wall, and compound wall causes cracks in building elements.
The following measures should be taken to prevent cracks in concrete arising from vegetation:
- Trees should not be planted very close to the walls of the building, compound wall. Shrubs should not be allowed to grow even in wall cavities.
- Trees, grasses, etc. should be cut down before starting new construction,
Cracks in concrete PPT
Also read:
- 14 Different Special Types of Concrete || Prons and Cons
- 14 Different Types of Mortar | Uses | Properties | Proportion
- 7 Major Causes of Foundation Failure in buildings || Types of foundation failures

I am a Professional Civil & Structural Engineer having more than 4 years of experience in Engineering, Procurement and Construction industry. Here i sharing the latest updates of EPC Projects and Construction News.

