In this article, we explained what is geosynthetics, types of geosynthetics, function of geosynthetics, application and benefits of geosynthetics on road. and so more. so please read the article till the end.
| Like us on Facebook | Click Here |
| Join our Telegram Group | Click Here |
| Subscribe us on YouTube | Click Here |
| Follow us on Google News | Click Here |
Table of Contents
What is Geosynthetics?
Geosynthetics are the key components of a system or structure that is used to achieve various engineering aspects or purpose.
Generally, Geosynthetics products are made from polymeric material. Geo means the Earth which represents the soil where the synthetics represent the polymeric material or synthetic materials.
From the name we can understand, the synthetic material which is used to increase the stability of soil is known as geosynthetics.
Various types of geosynthetics materials are used for various purposes like reinforcement, filtration, separation, drainage, water barrier, etc.
Geosynthetic materials are used in Soil related projects of construction. Like it was mostly used in Road, railway, Dam, hydraulics, retaining wall, canal, marine structure, foundation, embankment, etc. construction projects related to soil in the civil engineering profession.
Also Read: Different Types of Cofferdam
Geosynthetics material is the most suitable material for inside ground usage due to its synthetics nature and high durability of that material.
The main objective of geosynthetics material is to increase the stability or strength of soil and to reduce cost of construction.
Functions of Geosynthetics
The Primary Functions of Gyosynthetics are listed below:
- Reinforcement
- Separation
- Filtration
- Drainage
- Moisture barrier
Soil Reinforcement
The soil reinforcement function ensures improved response of the soil to loading It increases normal loading and reduces disturbing shear forces.
As a result, steep slopes can be constructed or an embankment of increased height be built on soft soil, which otherwise would not have been possible.
Separation
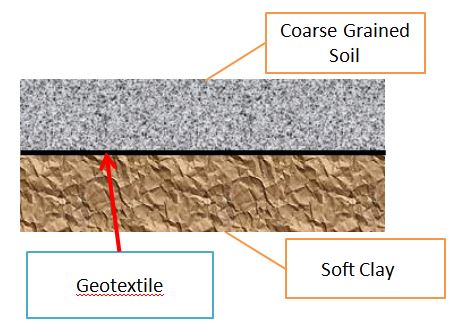
Geosynthetics are useful to separate dissimilar soils. A separator helps prevent intermixing of poor in situ soil with good quality granular materials when the structure is subjected to surface loading.
It acts as a barrier to the migration of particles between two dissimilar soils, a requirement in many applications such as pavements, graded filters, clay covers, and liners in landfills, etc.
Also read: How to construct Foundation in Black Cotton Soil
Filtration
Geosynthetics such as geotextiles allow the movement of a liquid across the plane of geotextile while retaining the soil on the upstream side.
To achieve this, the material should meet conditions of both adequate permeability, requiring an open fabric structure, and soil retention requiring a small opening size.
The long-term soil to geotextile flow compatibility is also important in that the filter must not clog excessively during its lifetime.
Drainage
The drainage function of geotextiles enables flow in the plane of geotextile. Apart from geotextiles that transmit the fluids, nowadays, their specific products such as geonets and drainage composite meet drainage requirements.
Barrier
The barrier function using geomembranes and geotextiles coated with bitumen is useful in many applications for minimizing fluid and vapor flow. It is useful in many applications such as canal linings, liquid impoundments, dams, municipal waste landfills, etc.
Types of Geosynthetics
the classification of geosynthetics based on materials are listed below.
- Geotextile
- Geogrid
- Geomembrane
- Geocell
- Geosynthetics Clay liners
- Geopipe
- Geofoam
- Geocomposite
1. Geotextile

Geotextiles are the synthetics products that consist of thin & strong membrane fabric.
Geotextiles are made from synthetic fibers such as cotton, wool, or silk, etc.
Geotextiles are made of flexible, porous fabric by standard weaving machinery or matted together in a random, or nonwoven manner.
Geotextiles are used in soil for separation, reinforcement, filtration, and drainage purposes.
Mostly geotextiles are used in soil for drainage function. And it is mostly used in road construction to make it more strong and durable.
Also Read: What is Stub Column?
2. Geogrid

Geogrids are polymeric materials that have a net or grid-like configuration. Due to its grid-like configuration, geogrid has a large opening which is known as apertures.
Geogrids are used for reinforcement purposes in soil, and it is commonly used in subbase of roads pavements.
Geogrids are made of a polymeric material such as polyester, polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene or propylene.
Geogrid materials are strong in tension and it transfers or distributes the load on large areas of soil surface which increases the stability of the soil.
Also read: Types of Caisson Foundation
3. Geomembrane

Geomembranes are the impervious thin sheets of plastic material that are used to cover liquid or solid storage.
Geomembranes are the most used geosynthetics material. And the main function of a geomembrane is to act like a liquid or vapor barrier.
Applications of Geomembrane:
- Geomembrane was used to control expansive soil.
- Geomembrane was used to control frost susceptible soils.
- It was used to prevent the infiltration of water in sensitive areas.
- It was used to form barriers as dams.
- It was used to contain seepage losses as a temporary cofferdam.
- Geomembrane is used as a liner for radioactive or hazardous waste liquid.
- Geomembrane is used as a liner for solar ponds, etc.
Also read: What is Monolithic Construction Technology?
4. Geocell

Geocells are the three-dimensional honeycomb cellular structured synthetic material that is filled with compacted soil to form a confined system.
Geocells are used for erosion control, soil stabilization, stability of steep slopes, and for earth retention, etc.
In research of geocell, it is found that geocell confined gravel bases are equivalent to the twice thickness of unreinforced gravel bases. And geocells are much better than geotextiles or geogrids.
Application of Geocells
- Geocells are used as a reinforcement material in the roadway.
- Geocells are used for steep soil slope and channel protection.
- Geocells are used for earth retention purposes.
- Geocells are used for protection of landfills.
Also read: Precast Concrete Vs Site Cast Concrete
5. Geosynthetics Clay liner

Geosynthetic clay liner consists of a liquid barrier material such as bentonite or other very low permeability material that is sandwiched between two geotextiles or bonded to a geomembrane with the help of needle punching or adhesives materials.
It was the newest subset of geosynthetics materials. And it was used as a water barrier.
6. Geofoam

Geofoams are lightweight large blocks that are made by processing polystyrene into a foam.
This was a lightweight and thermally insulating mass that is buried in the soil to achieve various engineering functions.
Geofoams are used for lightweight fills, green roof fills, compressible inclusion, thermal insulation, drainage, etc.
7. Geopipes

Geopipes are the type of geosynthetics material that is made from perforated or solid polymeric pipes and used for the drainage purpose of liquid or gas.
8. Geocomposites

Geocomposites are the composite material of geotextile, geogrid, geomembrane; which consist combination of geogrid and geotextile or geotextile and geomembrane, or geogrids, geomembrane and geotextiles or any of these three geosynthetics material.
Also any one of these three materials can be combined with another synthetic material such as soil.
Mostly geocomposites are used in soil for separation, reinforcement, filtration, drainage, or barrier function.
Properties of Geosynthetics
Physical Properties
- Specific gravity
- Unit mass
- Thickness
- Stiffness
Mechanical Properties
- Compressibility
- Tensile strength
Survivability Properties
- Tearing strength
- Static puncture strength
- Impact strength
- Bursting strength
- Fatigue strength
Also Read: Types of Under Reamed Piles
Major problems associated with weak deposits
- Low bearing capacity
- Higher settlement ( both total and differential )
- High seepage losses
- Liquefaction during earthquake
- Instability of foundation excavations
- Higher earth pressures on retaining structures
Benefits of Geosynthetics in roads
Advantages of geosynthetics use in roads are as follows:
- Improved performance
- Significant saving in cost
- Very good serviceability in both short and long term
- Possible to construct roads in difficult locations such as Marshy land, soft/organic deposits, expansive soil.
- Geotextile acts as a filter, prevents fines from migrating into aggregates
- Excess pore pressure dissipates through geotextile
- Subgrade soil gains strength through consolidation

I am a Professional Civil & Structural Engineer having more than 4 years of experience in Engineering, Procurement and Construction industry. Here i sharing the latest updates of EPC Projects and Construction News.

