In this article, we share the details of Laser crack Management system, what is this and how its is work, what are the benefits of LCMS in road and infrastructure industry and how it help to do maintenance of pavement at less time.
So read the article till the end, and if you get any valuable information from this than please share it with your friends.
Structural safety is a critical concern in engineering, and detecting cracks at early stage is difficult task for civil engineers.
Cracks in roads or buildings decreases the durability and lifespan of structures by deterioration of concrete or corrosion of reinforcement. These defects develop due to weather conditions, heavy traffic, and material fatigue. If cracks are not repaired, they expand and lead to costly repairs or structural failures.
So it is necessary to inspect the cracks at an early stage to avoid such problems. Identifying these cracks at an early stage is crucial for roads, bridges, and other infrastructure. The Laser Crack Management System provides an efficient solution for crack detection.
Table of Contents
What is a Laser Crack Management System?
LCMS is a technology that uses laser beams to detect, measure, and monitor cracks in materials like concrete, metal, and asphalt. It is widely used in infrastructure (bridges, roads), aerospace, energy (pipelines, wind turbines), and construction. Unlike manual inspections, LCMS provides precise, fast, and non-contact measurements.

LCMS is a one type of Pavement distress identification method which is more precise. Here are the few other techniques that is used to measure the pavement distress. These methods help engineers to assess road conditions and plan maintenance effectively. Some of the most common methods include:
- Manual Surveying: Engineers physically inspect roads and record observations.
- Photographic Imaging: High-resolution images are analyzed to detect surface defects.
- Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR): Examines subsurface issues that are not visible on the surface.
- Infrared Thermography: Identifies defects based on temperature variations.
Each method has its advantages, but LCMS stands out for its precision and efficiency.
How the Laser Crack Management System Works
LCMS scans road surfaces to detect cracks, potholes, and other defects. It uses high-speed cameras and laser sensors mounted on a vehicle that moves along the road. The collected data is processed to create a detailed map of road conditions. Here is the step by step process of how LCMS detect cracks.
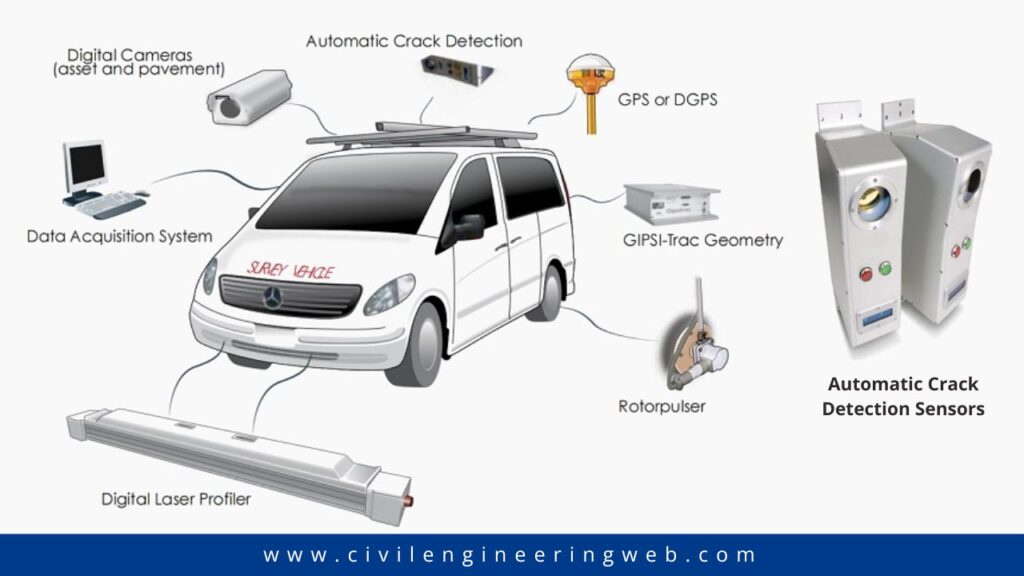
Step 1: Laser Scanning
A laser device emits a focused beam of light onto the surface being inspected. The laser can be handheld, mounted on a vehicle, or attached to a drone.
Step 2: Data Capture
When the laser hits the surface, it reflects or scatters. Cracks or defects alter the light’s behavior. Sensors (like cameras or photodetectors) record these changes.
Step 3: Data Processing
Software analyzes the captured data. Algorithms identify irregularities in the light patterns and convert them into crack measurements (length, width, depth).
Step 4: Visualization
Results are displayed as 3D maps, graphs, or heatmaps. Engineers use these visuals to prioritize repairs.
How LCMS Classifies Cracks
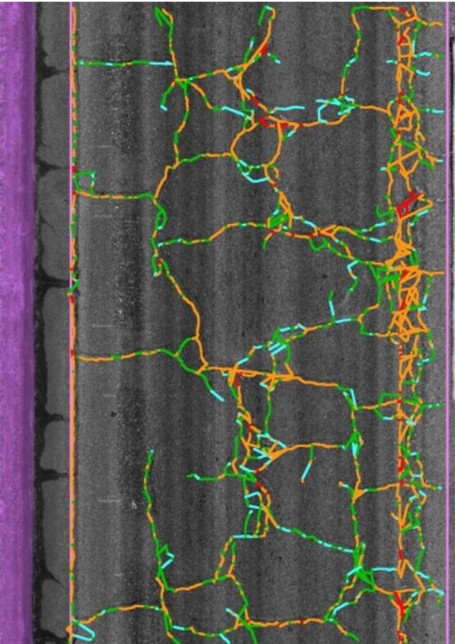
LCMS classifies cracks based on:
- Size and Depth: Measures crack width and penetration depth.
- Type of Crack: Identifies longitudinal, transverse, alligator, and block cracks.
- Severity: Categorizes cracks as minor, moderate, or severe.
The system uses contour-based and color-based analysis to visualize and interpret the severity of cracks. Engineers analyze this data to develop effective maintenance strategies.
Case Study: LCMS in Airfield Pavement Management
A case study conducted at Dublin and Cork Airports in Ireland to showcase the effectiveness of LCMS in airfield pavement maintenance. The study compared three different methods:
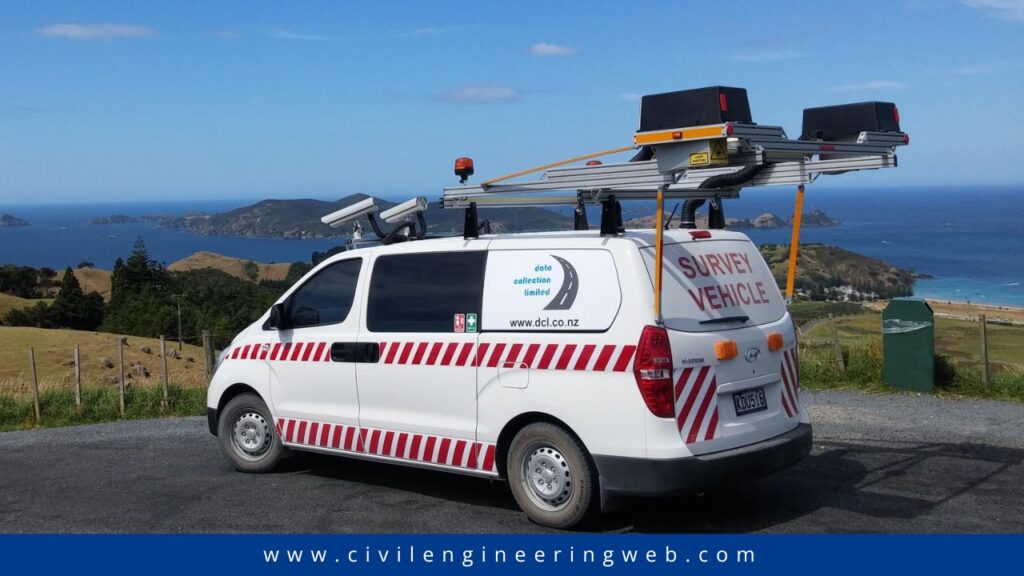

- Manual Inspection: Engineers manually assessed cracks and other defects.
- High-Definition Video Survey: A video system captured pavement surface images for later analysis.
- Laser Crack Management System: Automated sensors scanned the pavement surface and generated detailed reports.
Key Findings
- LCMS was able to complete the PCI survey within stringent time constraints between flight schedules.
- The system identified distress patterns more accurately than manual methods.
- Runway closures were significantly reduced, improving operational efficiency.
- The PCI values obtained using LCMS closely matched those derived from manual surveys, proving its reliability.
Reference:

I am a Professional Civil & Structural Engineer having more than 4 years of experience in Engineering, Procurement and Construction industry. Here i sharing the latest updates of EPC Projects and Construction News.

