Table of Contents
Blockchain: The Future of Smart City and Building construction.
Blockchains are expanding beyond finance and now seek to transform all industries, from healthcare to public administrations.
The construction sector is also beginning to study its potential benefits and, although this technology is still taking its first steps, there are already many experts who assure that its applications will be many and that they will go beyond transactions and smart contracts.
As in other areas, blockchains can increase the transparency and security of processes, and also help to improve supply chain management and favor buildings with a more sustainable and efficient useful life, among others. advantage.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain is a digital, decentralized (distributed) a ledger that keeps a record of all transactions that take place across a peer-to-peer network. It is an interlinked and continuously expanding list of records stored securely across a number of interconnected systems.
How Blockchain Work?
 |
| IMAGE SOURCE:- GOOGLE || IMAGE BY:- FICCI.IN |
Blockchain Technology Helps
Internet of things
“Internet of things [IoT] and blockchain are going to go hand in hand yes or yes,” says Clluc CTO Santiago Márquez. Since in construction any element can be sensed and replicated on the digital plane, blockchains can be the vehicle that guarantees its incorruptibility and transparency.
“You can put a sensor to a hammer, know who is using it and where and what breakdowns it has had,” exemplifies Márquez. The blockchain in charge of managing the information of this hammer would be the one that, in turn, would provide the guarantee that the data is truthful and has not been manipulated.
With the building already built, the sensors could be applied to measure its sustainability parameters.
“If the building is sensed, its energy efficiency can be controlled and secured with blockchain,” says PropTech Lab CEO Jorge Zanoletty. But this app can be taken on an even bigger scale: city building.
“If you have a blockchain platform that connects a smart city at all levels (transport, health, energy …) and a common technological layer that unites IoT, the interconnected city is a reality”, explains the coordinator of Blockchain Spain and co-author of the Blockchain book: the industrial revolution of the internet, Alex Preukschat. Dubai (United Arab Emirates) already has among its goals to become the first blockchain city by 2020.
Safer supplies
Another area of opportunity in blockchain construction is the raw materials supply chain. Many materials to be controlled are commissioned and administered at the works; some even run the risk of spoiling if not used in time.
“One of the problems has to do with concrete. From the moment it is purchased to the moment it is used, many things can happen that distort its properties. This has brutal costs,” explains Márquez. The blockchain can be used to manage these risks.
The expert points out: “With blockchain, we can follow the traceability of raw materials and control where they come from, where they go through and what controls have been carried out on them.” That fingerprint of the materials allows them to be recycled and reused more intelligently.
This is what IoT and blockchain-based construction software solutions company Intelliwave Technologies does.
The company has created SiteSense, a private blockchain platform that “is already being used in construction projects around the world,” says CTO and company co-founder Jordan Williams. The manager expands: “We couple our technology with sensors to track each activity, materials, equipment and registration documents throughout the life cycle of the project.
This serves to automate and validate transactions more quickly, accurately and reliably, and to connect all stakeholders. ”
Another advantage is that it also “enables the exchange of critical information in real-time,” says Williams, citing the following example: “If a purchase of a large refrigeration unit is approved, the details are immediately shared with the supplier and the production team also sees the transaction.
The BOM, shipping dates are updated, and workers know when they can use it. When the purchase arrives, it is automatically logged. ”
Locked information
BIM (Building Information Modeling) software is booming and many companies are starting to use it as a standard. However, the information produced is often lost when the project is delivered. Combining BIM with blockchain could avoid this problem.
“With a blockchain platform, the building can be fully traced: how it has been built, what its technical specifications are, where the materials have come from, what they are and where they are placed. In this way, throughout the life of the project (in use, maintenance, and even demolition), there would be an immutable, transparent, easy and inexpensive information resource that would make its use more efficient, “says Zanoletty.
Blockchain can also help protect intellectual property: “When designing in BIM, constructive elements are added, such as a digital beam. Until now, the authors had no control over what they had created and anyone could appropriate and modify it.
The chain of blocks allows to give these elements an unalterable and non-transferable digital footprint “, explains Zanoletty. “Combining BIM and blockchain opens up an unfathomable source of resources,” he adds.
A digital notary
One of the main characteristics of the blockchain is that it eliminates the need for an intermediary in certain processes. This is how the concept of smart contracts or smart contracts arises, something that is being developed in many sectors and which also have their place in buildings.
“Blockchain is a technology in which someone can reach an agreement with another person, without anyone having to mediate, for free, instantly and guaranteed for life,” explains Visual Technology Lab co-founder Iván Gómez.
“There are a lot of little deals under construction where you don’t have to have a human notary and where blockchain can act as a digital notary,” he says.
“It will be something that can be applied in actions associated with the building management process and the mechanisms for issuing and validating work certifications,” confirms the director of business development at the Official College of Quantity Surveyors and Architects of Madrid (Spain), Felipe Aparicio.
In turn, its use has become very popular for property registration. For example, in Sweden, real estate transactions are already being carried out between all the agents involved with blockchain.
“In countries where there is corruption or lack of guarantees to maintain ownership, this becomes critical,” says Zanoletty. The Bitland company is implementing it in Ghana.
“There are frequent disputes over land ownership there, so we thought about using blockchain,” explains CSO Chris Bates.
In addition to brawls, the inability of registries to update in real-time “enables a perfect scenario for fraud and slows economic development; blockchain prevents it and improves transparency,” says Bates. They are now working with the Lakota tribe in South Dakota (USA).
Union make force
As all of these initiatives demonstrate, the key to the blockchain is its union with other technologies. “If you unite BIM, IoT, and blockchain you can get a virtual twin of the physical building; a lot of information through sensors on lights, air conditioning, and heating; and a platform where to store that data in an immutable, cheap and indelible way,” he explains. Zanoletty.
For his part, Gómez wants to combine smart contracts with virtual, augmented reality and BIM.
“Blockchain is used to create smart contracts, which reflect the agreements that are made daily in construction and collect the changes that must be carried out in a work that has just been delivered to the client. With virtual and augmented reality, you can mark the flaws, taking the BIM model as a reference for the repairman to locate them digitally.
Everything would be automatically registered, “he details.
Although there are many ideas on the table to use blockchains, not all of them go beyond a theoretical approach.
“Right now, everything exists on a prototype level, but still nothing is working massively,” says Preukschat. Despite this, the practical potential of blockchain is undoubted and that is why “almost all the large companies in Spain are studying how to improve their processes with blockchains,” says Márquez.
What does it take to boost it? “That the regulation and the laws are brought up to date”, thinks Gómez.
Advantages of Blockchain Technology
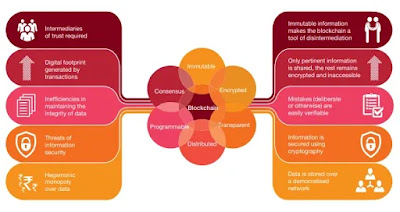
- Blockchain is a distributed network that stores information in the tamper-proof form which can only be appended but not modified by valid ‘users’. In order to understand the full potential of the blockchain, one needs to understand the basic attributes of blockchain which makes this technology unique:
 |
| IMAGE SOURCE:- GOOGLE || IMAGE BY:- FICCI.IN |
- The blockchain holds the potential to disrupt any form of transaction that requires information to be trusted. This means that all intermediaries of trust, as they exist today, are exposed to being disrupted in some form with the advent of blockchain technology.
- The figure below shows how blockchain technology is resolving problems with the way information-related transactions occur today.
- The boxes on the left illustrate key issues, while those on the right depict how blockchain technology helps address them.
 |
| IMAGE SOURCE:- GOOGLE || IMAGE BY:- FICCI.IN |
Understanding Blockchain& Smart contracts4 Ways Blockchain Will Change Construction Forever
https://hbr.org/2019/07/how-blockchain-will-change-construction

